Understanding DC Amperage: What It Is & How to Measure It Accurately
Understanding DC Amperage: What It Is and How to Measure It
Direct Current (DC) plays a vital role in our everyday lives—from powering small electronic devices to running large-scale battery systems in solar setups and electric vehicles. Understanding DC Amperage and knowing how to measure it accurately is essential for professionals, hobbyists, and DIY enthusiasts alike.

What Is Direct Current?
Direct Current (DC) is the flow of electric charge in one consistent direction. Unlike Alternating Current (AC), where the flow reverses periodically, DC maintains a constant polarity. It’s typically supplied by batteries, solar panels, and DC power supplies.
You’ll find DC Amperage in devices like:
- Smartphones and laptops (via their internal batteries)
- LED lighting
- Solar energy systems
- Electric vehicles
- Circuit boards and low-voltage electronics
Why Measuring DC Amperage Is Important
Whether you’re diagnosing a power issue, building a circuit, or maintaining a battery system, measuring DC amperage can help you:
- Detect overloads
- Check battery health and charge/discharge rates
- Verify circuit performance
- Ensure proper current flow in sensitive electronics
Incorrect current can lead to component damage, overheating, or underperformance.
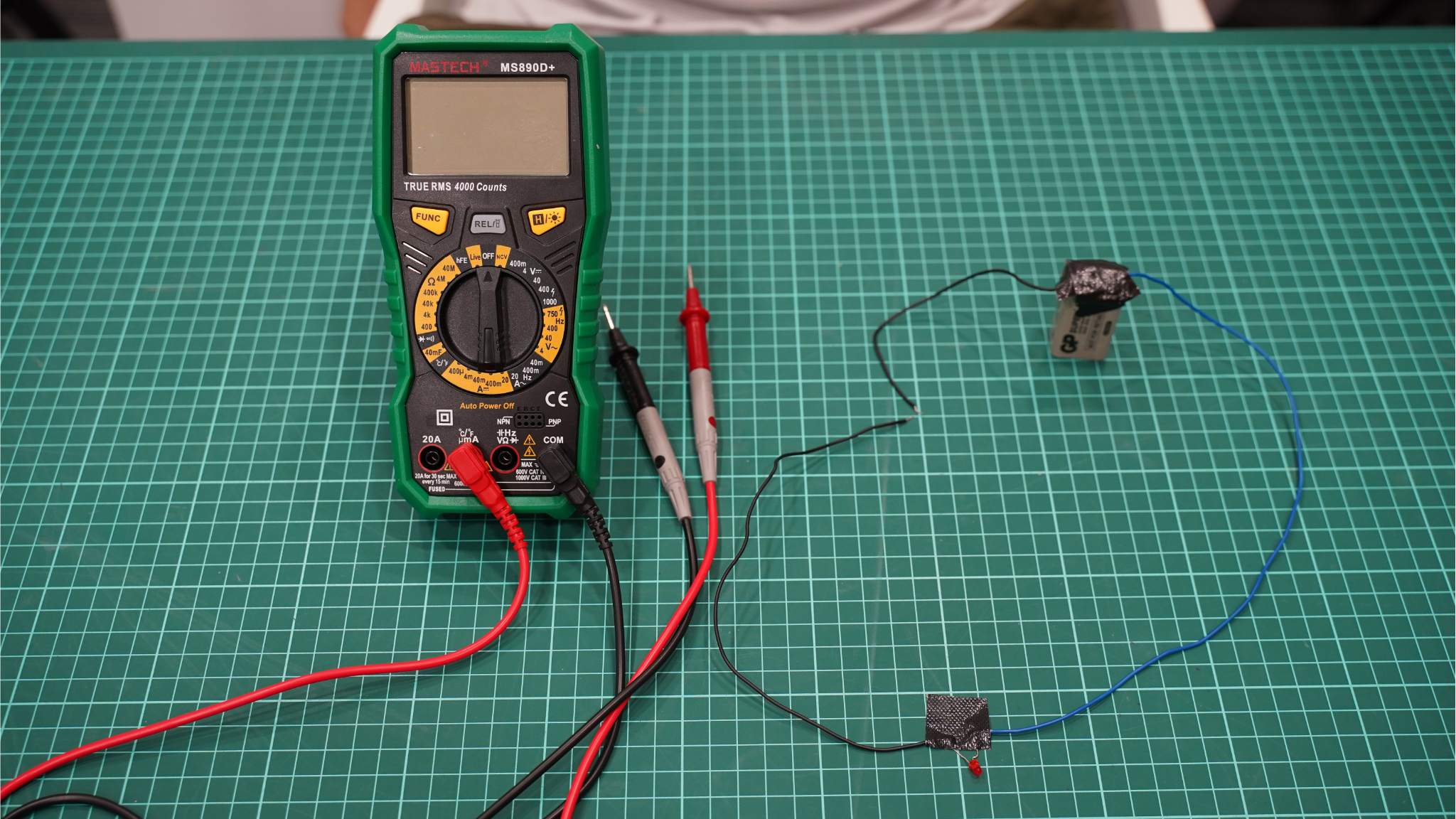
How to Measure DCA Using a Digital Multimeter (DMM)
1. Turn the dial to the DC Amperage (DCA) setting.
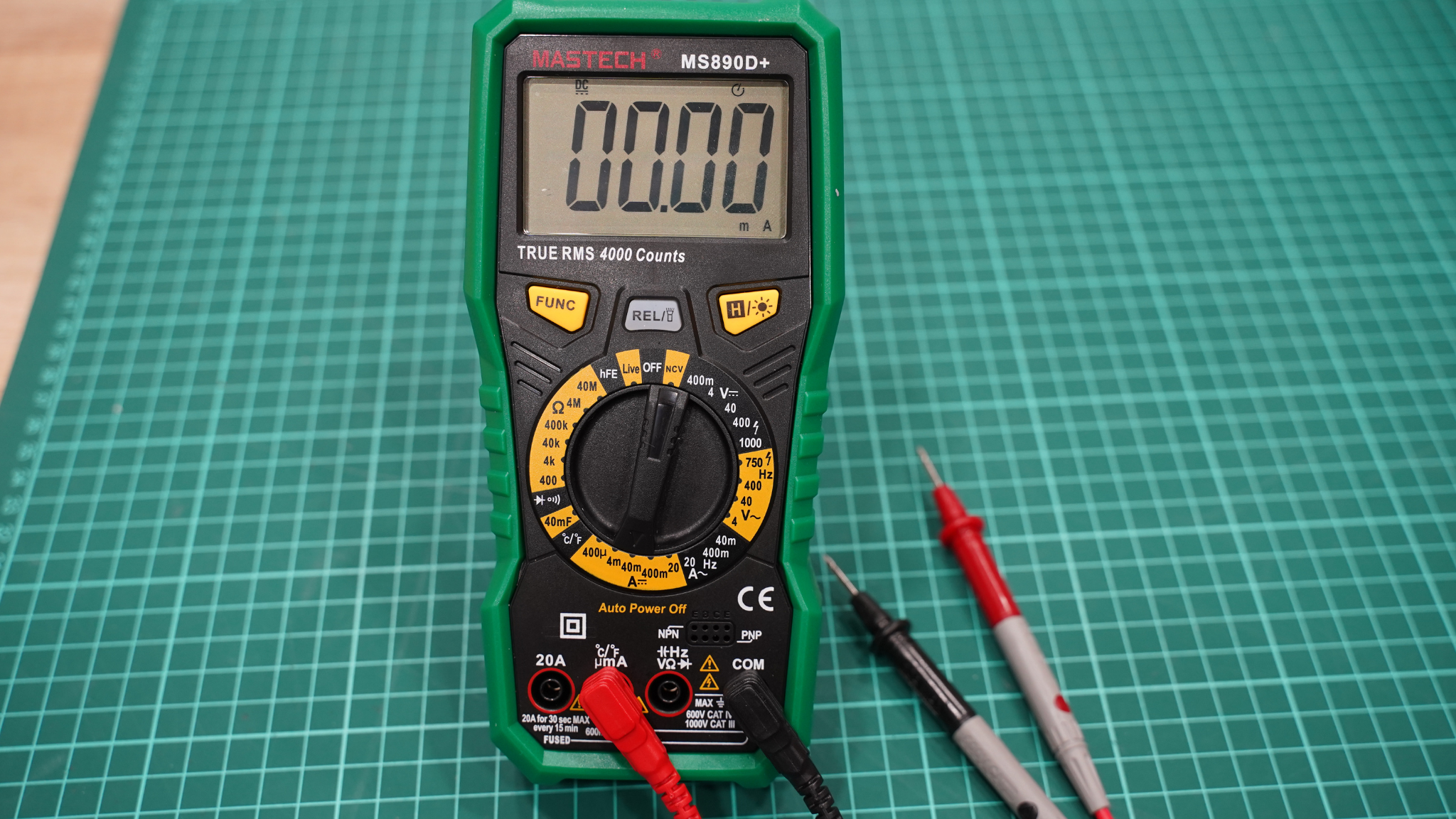


2. Insert the test leads:
- Black lead into the COM port
- Red lead into the A (or mA/μA) port depending on expected current range
3. Break the circuit where you want to measure current. Remember, current measurement must be done in series.
4. Connect the leads in series—red lead to the positive side, black lead to the negative side.
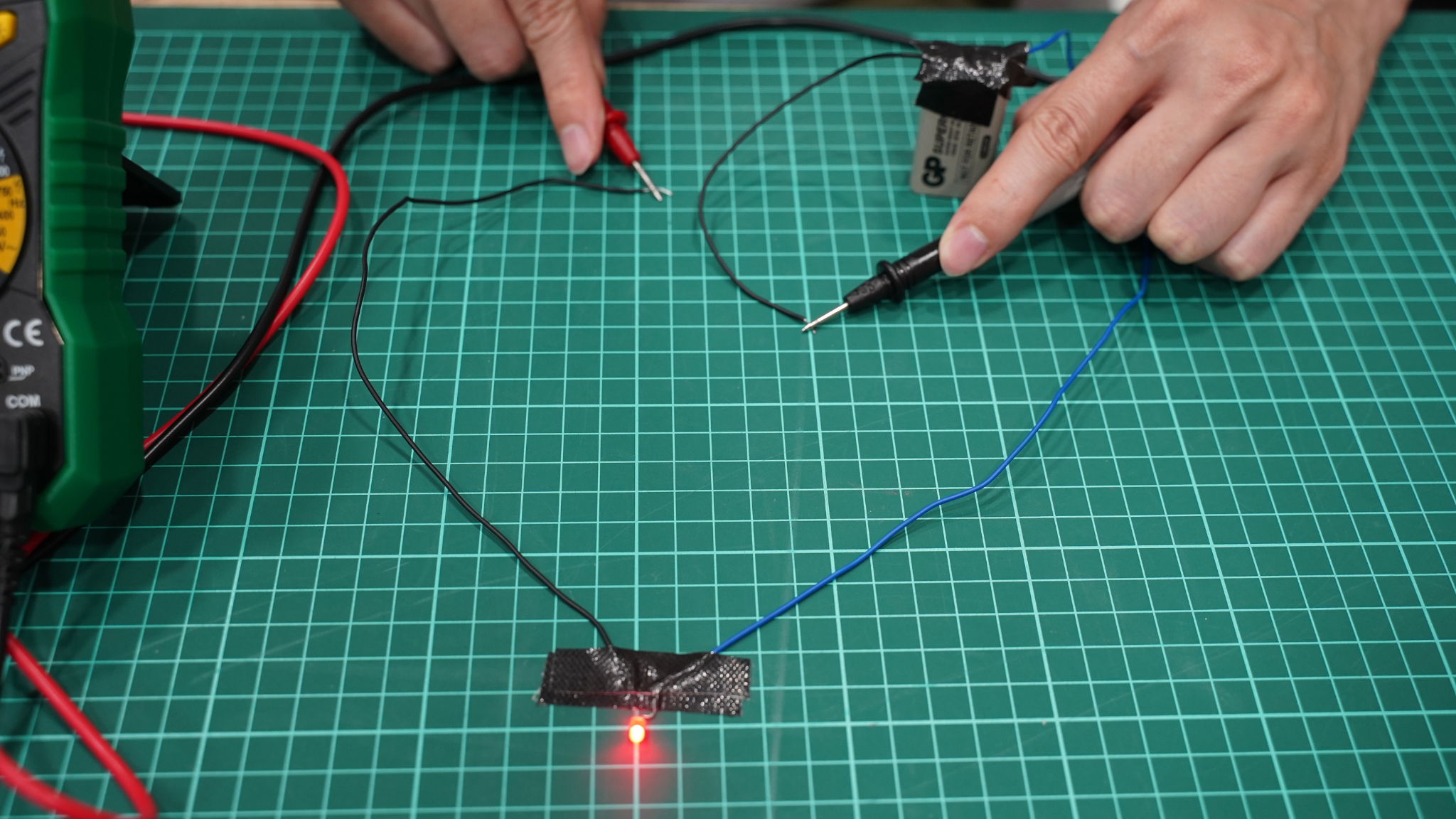

5. Read the value on the screen.
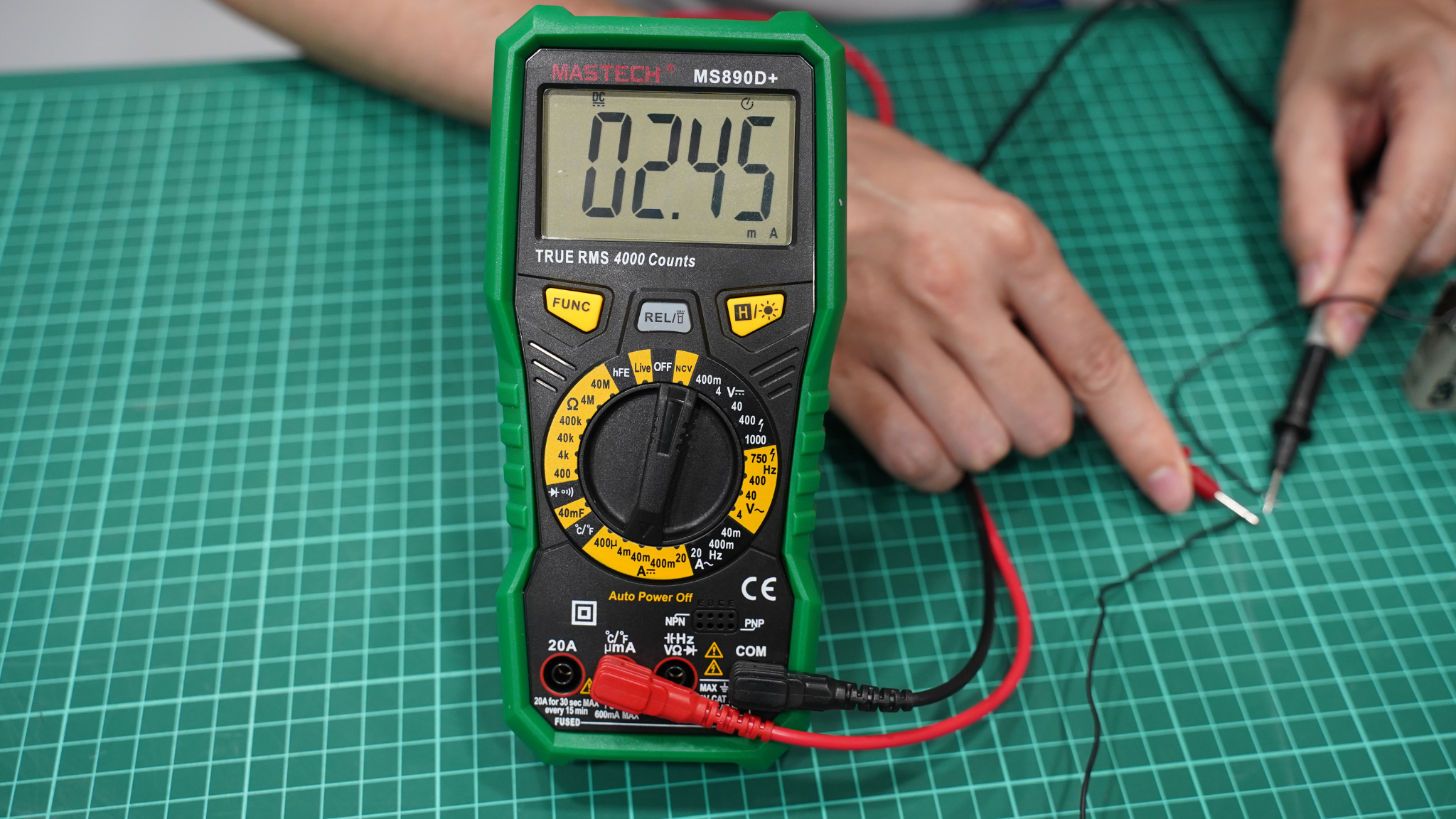


Important: Always start with the highest current range first to avoid damaging your meter.
Tips for Accurate Measurement
- Always double-check the current range and connection points.
- Use the correct port to prevent blown fuses in the meter.
- Avoid measuring current in high-voltage circuits without proper knowledge or safety equipment.
- If you're unsure of the expected current, use a clamp meter to safely estimate it.
Conclusion
DC current is all around us—from small circuits to solar installations. With the right tools and techniques, measuring it is straightforward and incredibly useful for troubleshooting and maintaining electronic systems.
Whether you're using a multimeter or a clamp meter, understanding how to properly measure DC current will help you work more confidently and safely.
2025-05-23

 Mastech CN
Mastech CN Mastech TW
Mastech TW